
This post will save you $1200 USD (or, why virtual conferences have been so disappointing).
by Future Historian October 21, 2021Yes, this post will save you $1,200!
That’s $1,200 in the cost of registration and the cost of your time that you don’t have to spend!
Before I get into the specific results, I want to go up on a soapbox. Over the past two years, the virtual conferences I’ve been a part of, both as a presenter and as an attendee, have been uniformly lame.
This is nothing against the specific organizers! I’ve was actually on the organizing committee for one of them. It’s just that this time of COVID has really crystalized what I find the most valuable at professional conferences. It’s not the session or the presentations. Is there anything less engaging than PowerPoint slides on a webinar?
What is valuable are the conversations that happen in the hallways between the sessions. It’s the breakfasts, the lunches, the dinners, and all the thinking and connection that get facilitated by being in the same spot. And that hasn’t happened online.
And yet, I recognize that there are huge benefits to virtual conferences in terms of access. Most people cannot travel nationally or internationally to attend conferences. This is a major equity issue. People can’t afford the cost of being exposed to new ideas and opportunities. For those of us with a specific mission to get these ideas out there, well, this ain’t so good.
Despite a year of practice, I personally haven’t seen anything in the second wave of virtual conferences that have addressed the fundamental need for human connection. And this is actually kind of weird!
There are plenty of online communities where ideas and content are vibrantly shared. Reddit! Discord! You could even start a Facebook page. Why this interactive dynamic has not yet been cracked for the academic conferences is kind of a mystery.
Quick digression. PubTrawlr has started a Discord Server. Let us know if you want to join!
There are some platforms that mimic massive multiplay online gaming (MMPORG), like VirBela, which empowerment evaluation guru David Fetterman is a big fan of. But still, they’re at a small scale.
But how can I save money?
This brings me to the cost-saving part of this post. The 14th Annual Dissemination and Implementation Conference will be held in about two months. Conference theme: “Broadening Horizons for Impact: Incorporating Multisectoral Approaches into D&I Science.” This conference is generally this high-water mark for implementation research for the year. This is where there the most rigorous studies get submitted and discussed.
And, it’s usually the most expensive. When in-person, it runs upwards of $600 for two days. Now that it’s virtual, it’s only $300. But what are you paying for if the best part, the connections, aren’t present? And then you add the lost time sitting in front of a screen watching slide after slide…it adds up.
All the abstracts are freely available online. So, in service to you, the cash-strapped practitioners, we decided to apply some old PubTrawlr magic to the content to let you know, in advance, what you’d get if you chose to attend. The only thing you’d been missing is the slides!
There are 115 sessions across nine tracks. Now, with break-out sessions, you can’t possibly attend them all. But now you can!
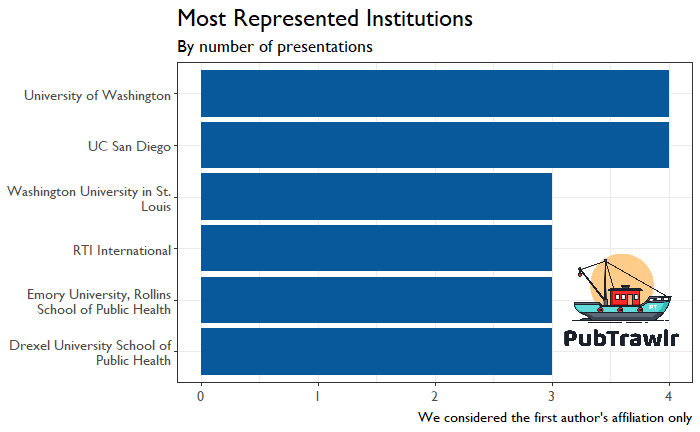
First off, let’s look at the presenters, which we grouped by the institution. The usual suspects are going to be here. We didn’t dig into the other authors and their affiliations to keep things straightforward.
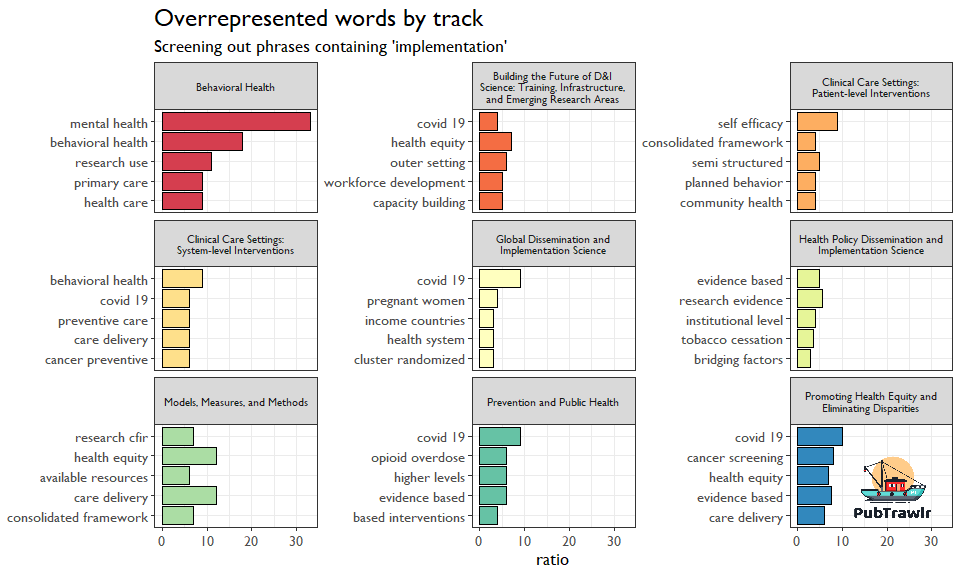
Then I started to dig into the session’s abstracts. Using a technique I picked up from Emil Hvitfeld, I looked for words that were overrepresented in each track compared to all other tracks combined (which is why some terms are duplicated) We can see some basic trends here in what the tracks are going to cover.
Topic Clusters
I then looked at the ways the different topics were clustered. I used the LDA method followed by a UMAP dimensionality reduction which color-coded each individual session by cluster. (Plenty of previous posts cover the nuts and bolts of this method.) I started with nine clusters because that’s how many tracks there are.
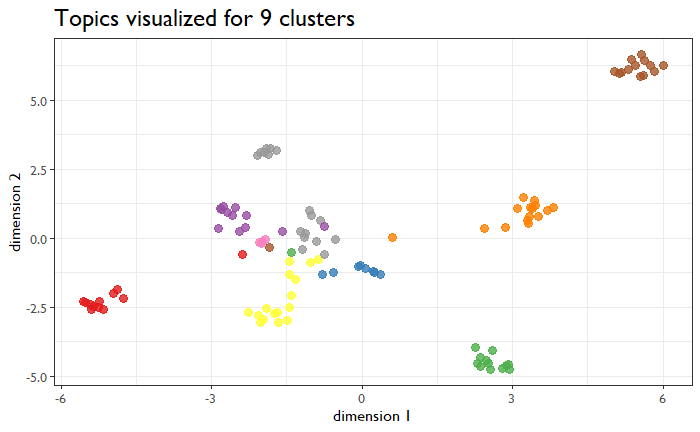
That doesn’t quite look right. There’s some mush in the middle. Also, there is an extra small pink cluster hiding in the middle of that mush. This is maybe six-ish clusters, so I tried that configuration.
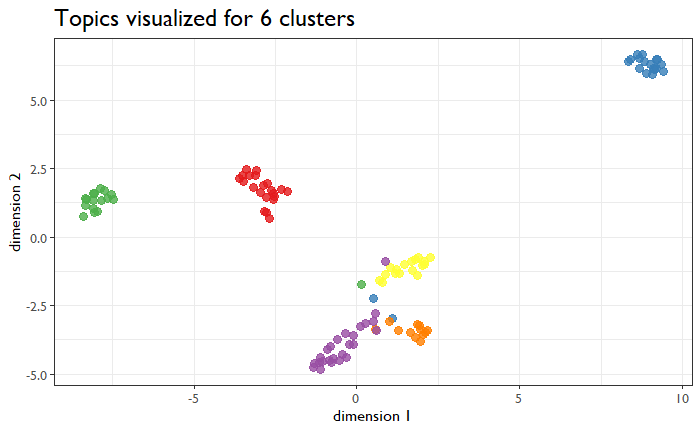
Much better. There are still some abstracts that don’t fall in nicely, but overall this seems to be a good grouping. I then pulled out the distinguishing words for each of these six topics and then counted home many abstracts were represented for each cluster. What do you know? Our good friend CFIR is up at number 1.
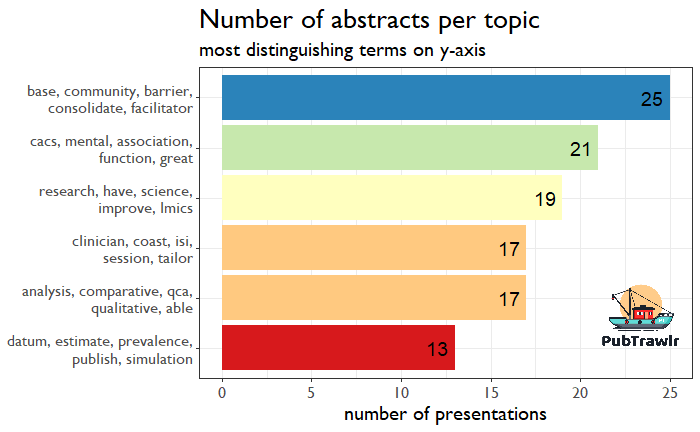
Topic Summaries
Okay, but what are you specifically missing out on? Well, read the summary descriptions below! These are generated by finding the sentences that are linguistically best representative of all sentences within a cluster, then arranging these in descending order like a newspaper would do. The readability is a bit meh, but it does a fair job of communicating the gist.
| Distinguishing terms | Abstractive Topic Summary |
|---|---|
| cacs, mental, association, function, great | Greater leadership engagement, more positive implementation climate, and having more available resources (e.g., staff/training/time) were all significantly associated with greater adoption of TIC training and staff support practices. Leadership and Organizational Change for Implementation (LOCI) is a multifaceted implementation strategy to support the implementation and sustainment of EBPs. By engaging and developing leadership at clinic and organization levels, LOCI aims to develop a climate for EBP implementation and sustainment within organizations. Mental health screening and referral protocols can increase accurate identification of children’s mental health needs and facilitate access to evidence-based treatment but are infrequently used in CACs. This study tests associations between teamwork quality and implementation outcomes during a statewide initiative to implement a standardized screening and referral protocol for traumatic stress and suicidality in CACs. MDT members (N = 433) from 21 CACs completed 5 validated team functioning measures (Affective: liking/trust, psychological safety; Behavioral: learning behavior, coordination about mental health care; Cognitive: clear direction) and 2 team performance measures (overall performance; mental health care quality). Implementation timing varied across CACs; the survey occurred 1-18 months after initial training.The first three models tested associations of team functioning with implementation outcomes (acceptability, appropriateness, feasibility). |
| research, have, science, improve, lmics | Teaching for Implementation: A framework for building implementation research and practice capacity within the translational science workforce. Manuscripts in the JCTS special issue on D&I Research described (1) innovative strategies and frameworks designed to enhance and improve the translation of research to practice; (2) opinions of D&I researchers and CTSA leaders as to which strategies to could promote team science and improve population health; (3) partnerships between academic and public health systems; (4) stakeholder engagement; (5) workforce development. Despite this, there is a lack of funding, training and mentorship for NCD investigators in LMICs. To address this, participants from the Global Research on Implementation and Translation Science (GRIT) consortia of studies in eight LMICs and their networks, attended the dissemination and implementation (D&I) massive open online course (MOOC) developed by the Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases at the World Health Organization to strengthen capacity building and D&I research concepts. Framework recommendations provide researchers with a needed tool to advance policy D&I research methods. |
| clinician, coast, isi, session, tailor | Leadership and Organizational Change for Implementation (LOCI) is a packaged and multifaceted implementation strategy that was developed to support the implementation and sustainment of EBPs. This presentation will review the core principles and components of the LOCI implementation strategy, as well as discrete capacity-building strategies that were employed by participating leaders to develop a climate for EBP implementation and sustainment within their organizations. The Collaborative Organizational Approach to Selecting and Tailoring Implementation Strategies (COAST-IS) is an implementation intervention that targets organizational leaders’ and clinicians’ ability to select and tailor implementation strategies that address their site’s needs. The aims of this study are to 1) present an implementation support intervention (ISI) developed by an Intermediary/ Purveyor Organizations (IPO) which uses the ‘EPIS’ Implementation framework to facilitate co-production in HIV service change projects and 2) explore the impact of the ISI on implementation outcomes and organizational structure. COAST-IS involved site-visits, 5 virtual educational sessions, and 12 coaching sessions which led leaders and clinicians through the Implementation Mapping process (e.g., identifying implementation outcomes, performance objectives, determinants, implementation strategies, and mechanisms). |
| base, community, barrier, consolidate, facilitator | Interviews were based on the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research and investigated perceived barriers to and facilitators of MAPS delivery by community health workers. The six-step systematic planning process included conducting a needs assessment, selecting determinants based on SARS-CoV-2 testing behaviors, barriers and facilitators, and identifying evidence-based strategies (e.g. use of role modeling of accessing testing and testimonials for testing success stories).To accelerate development of implementation strategies, we simultaneously developed program design components based on knowledge and evidence from previous community-based behavioral health interventions (e.g., use of community health workers, CHWs, social marketing strategies, and health coaching to address psychosocial and healthcare access barriers); thus using a “right to left and left to right” approach to development of strategies. This study presents findings from pre-implementation research guided by the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) to develop system-wide implementation strategies for the clinic-based implementation of a behavioral health screener and eHealth positive affect intervention for people living with HIV and depression. Using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR), we conducted 11 semi-structured 60-min interviews with community pharmacists. |
| datum, estimate, prevalence, publish, simulation | Our team used RCSM to: (1) analyze published evidence on perinatal depression screening, initially focusing on implications of screening results for understanding prevalence; (2) conduct study-specific simulations to estimate prevalence, supplemented by estimates of sensitivity and specificity from published meta-analyses; and (3) evaluate initial simulation models for potential insights to inform further implementation and evaluation. Using inter-organizational data to examine a disparity in multiple contexts, including care delivery and payment, enables stakeholders to better understand limitations of existing data, identify complementary data resources, and specify needs for future data collection and integration. |
| analysis, comparative, qca, qualitative, able | Approaches able to generate context-sensitive yet robust evidence about the causal relationships between care delivery implementation, practice, and outcomes include hybrid implementation-effectiveness research design, comparative case study methodology, interrupted time series (ITS) analysis, and qualitative comparative analysis (QCA). Qualitative comparative analysis (QCA), a type of CCM, was utilized to uncover configurations of CFIR contextual factors that are key to PrEP implementation success in family planning clinics. |
But let’s say you’re old school, and want to stick just with the topic track as specified. We got you covered too. Here are Track-based summaries, with no post-hoc clustering added.
| Track | Track Summary |
|---|---|
| Behavioral Health | Mental health screening and referral protocols can increase accurate identification of children’s mental health needs and facilitate access to evidence-based treatment but are infrequently used in CACs. This study tests associations between teamwork quality and implementation outcomes during a statewide initiative to implement a standardized screening and referral protocol for traumatic stress and suicidality in CACs. MDT members (N = 433) from 21 CACs completed 5 validated team functioning measures (Affective: liking/trust, psychological safety; Behavioral: learning behavior, coordination about mental health care; Cognitive: clear direction) and 2 team performance measures (overall performance; mental health care quality). Our findings suggested that schools should strategically intervention on staff ’s intentions to implement to amplify the effectiveness of common implementation strategies such as training and follow-up consultation, which will lead to favorable changes in implementation behaviors (e.g., fidelity) and client behavioral outcomes. This study presents findings from pre-implementation research guided by the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) to develop system-wide implementation strategies for the clinic-based implementation of a behavioral health screener and eHealth positive affect intervention for people living with HIV and depression. |
| Future of D&I Science: Training, Infrastructure, and Emerging Research Areas | Teaching for Implementation: A framework for building implementation research and practice capacity within the translational science workforce. Manuscripts in the JCTS special issue on D&I Research described (1) innovative strategies and frameworks designed to enhance and improve the translation of research to practice; (2) opinions of D&I researchers and CTSA leaders as to which strategies to could promote team science and improve population health; (3) partnerships between academic and public health systems; (4) stakeholder engagement; (5) workforce development. Investment in scientific workforce can close gaps in D&I research across CTSAs. The members of the Advancing D&I in CTSAs Working Group convened two working groups to develop recommendations for training the scientific and practitioner workforces in D&I competencies. |
| Clinical Care Settings: Patient-level Interventions | After TWP implementation 655 Veterans at the 4 pilot sites received telehealth for wound care. TWP implementation evaluation was guided by the Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation and Maintenance (RE-AIM) framework. |
| Clinical Care Settings: System-level Interventions | Leadership and Organizational Change for Implementation (LOCI) is a multifaceted implementation strategy to support the implementation and sustainment of EBPs. By engaging and developing leadership at clinic and organization levels, LOCI aims to develop a climate for EBP implementation and sustainment within organizations. Leadership and Organizational Change for Implementation (LOCI) is a packaged and multifaceted implementation strategy that was developed to support the implementation and sustainment of EBPs. This presentation will review the core principles and components of the LOCI implementation strategy, as well as discrete capacity-building strategies that were employed by participating leaders to develop a climate for EBP implementation and sustainment within their organizations. We also examined the relationship between organizational factors from the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (i.e., leadership engagement, implementation climate, and available resources) and adoption of TIC practices. |
| Global Dissemination and Implementation Science | In Stage 1, study staff conducted monthly SAIA visits and collected HTC data for 12 months. This cluster-randomized trial was conducted in 24 family planning clinics in Mombasa County with 1:1 randomization to either the SAIA implementation strategy or standard care. We conducted continuous quality improvement (CQI) meetings twice monthly for three months with healthcare workers (HCWs) involved in mobile phone delivery of the ATP at 10 intervention sites. |
| Health Policy Dissemination and Implementation Science | Policy D&I is an emergent research area which should be leveraged to increase the use of evidence in health policy and to investigate downstream health outcomes related to policy change. Bridging the translational gap between non-partisan research evidence and health policy in state legislatures requires understanding the systematic barriers to non-partisan research evidence use. The aim of this study is to explore the barriers and facilitators to fidelity implementation of APL policy among California Medi-Cal MCPs using the Exploration, Preparation, Implementation, Sustainment (EPIS) framework. |
| Models, Measures, and Methods | Frameworks that capture organizational constructs (e.g., environmental context and resources) exist (e.g., Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research; Theoretical Domains Framework), but their influence on implementation often remains a ‘black box.’ Limited understanding of how and why organizational constructs influence implementation is needed to improve implementation outcomes. Understanding dynamic change of implementation strategies over time within and across healthcare intervention efforts is critical to implementation science. Interviews were guided by constructs from the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR). |
| Prevention and Public Health | Using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR), we conducted 11 semi-structured 60-min interviews with community pharmacists. The Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) is a meta-theory comprised of constructs that have been associated with effective implementation. We also identified factors from the external and internal setting that were associated with higher levels of naloxone distribution. |
| Promoting Health Equity and Eliminating Disparities | Our use of IM and community engagement facilitated a process for rapid adaptation of materials and implementation planning strategies to reflect changes in the environment and community preferences, an approach we refer to as the “Community Just in Time Adaptive Intervention – Community JITIAI.” This simultaneous process supported rapid development of theoretical and evidence-based multi-level implementation strategies. The six-step systematic planning process included conducting a needs assessment, selecting determinants based on SARS-CoV-2 testing behaviors, barriers and facilitators, and identifying evidence-based strategies (e.g. use of role modeling of accessing testing and testimonials for testing success stories).To accelerate development of implementation strategies, we simultaneously developed program design components based on knowledge and evidence from previous community-based behavioral health interventions (e.g., use of community health workers, CHWs, social marketing strategies, and health coaching to address psychosocial and healthcare access barriers); thus using a “right to left and left to right” approach to development of strategies. The aims of this study are to 1) present an implementation support intervention (ISI) developed by an Intermediary/ Purveyor Organizations (IPO) which uses the ‘EPIS’ Implementation framework to facilitate co-production in HIV service change projects and 2) explore the impact of the ISI on implementation outcomes and organizational structure. |
Summing Up!
Hope this is helpful! And if you want to keep digging further and spend some of your savings, don’t forget about us on PubTrawlr. We’re on the cutting edge of getting the science out of the journals and into the hands of people who can do something about it.


Here’s an addedum to this post. I’ve been at APHA the last two days in person and it has been fantastic. People are masked, vaccine cards have been checked, and I’m actually getting real human connection with people.
I get all the arguments in favor of virtual conferences, but as a human animal, I love being around people.